Software Testing
Software testing is the process of assessing the functionality of a software program. The process checks for errors and gaps and whether the outcome of the application matches desired expectations before the software is installed and goes live.

Why Software Testing is important ?
There are various reasons, why a software may need modifications, few important reasons out of them are briefly mentioned here -
- Identifies defects early- Developing complex applications can leave room for errors. Software testing is imperative, as it identifies any issues and defects with the written code so they can be fixed before the software product is delivered.
- Improves product quality - When it comes to customer appeal, delivering a quality product is an important metric to consider. An exceptional product can only be delivered if it's tested effectively before launch. Software testing helps the product pass quality assurance (QA) and meet the criteria and specifications defined by the users.
- Increases customer trust and satisfaction-Testing a product throughout its development lifecycle builds customer trust and satisfaction, as it provides visibility into the product's strong and weak points. By the time customers receive the product, it has been tried and tested multiple times and delivers on quality.
- Detects security vulnerabilities - Insecure application code can leave vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Since most applications are online today, they can be a leading vector for cyber attacks and should be tested thoroughly during various stages of application development. For example, a web application published without proper software testing can easily fall victim to a cross-site scripting attack where the attackers try to inject malicious code into the user's web browser by gaining access through the vulnerable web application. The nontested application thus becomes the vehicle for delivering the malicious code, which could have been prevented with proper software testing.
- Saves money - Software development issues that go unnoticed due to a lack of software testing can haunt organizations later with a bigger price tag. After the application launches, it can be more difficult to trace and resolve the issues, as software patching is generally more expensive than testing during the development stages.
Testing Classifications
All types of testing can be classified into two types - Functional Testing and Non-Functioanl Testing
- Functional Testing - Functional testing is a type of testing that seeks to establish whether each application feature works as per the software requirements. Each function is compared to the corresponding requirement to ascertain whether its output is consistent with the end user's expectations.
- Non-Functional Testing - Non-functional testing assesses application properties that aren't critical to functionality but contribute to the end-user experience. Performance and reliability under load aren't functional components of a software system but can certainly make or break the user experience
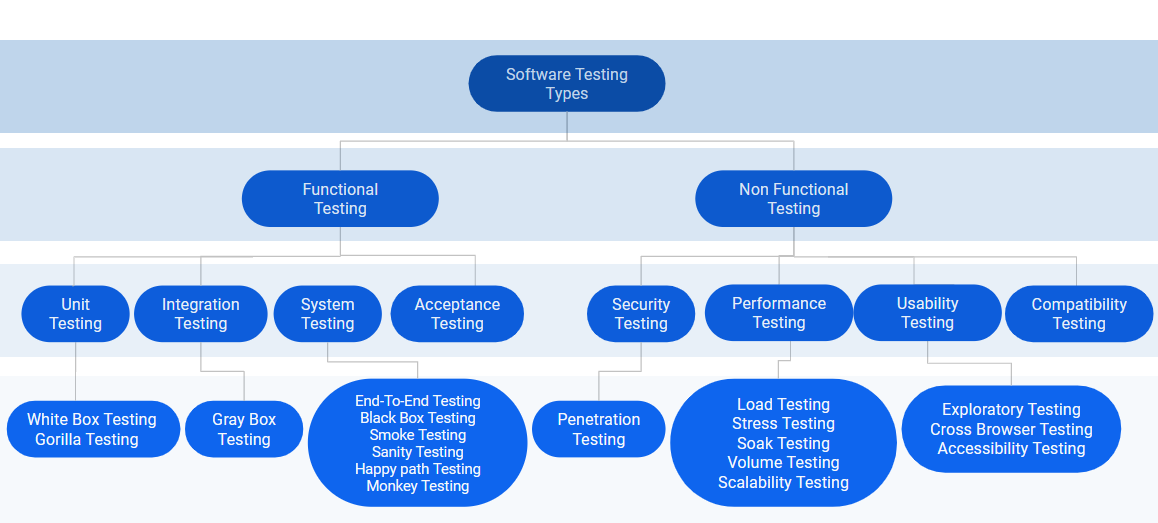
Various Testing We Perform
Unit testing
Ensures each individual unit or component performs as expected. Its typically conducted during the app development phase.
Features Testing
Check each function against functional requirements. A blackbox test is a common example.
Integration Testing
Groups together two or more modules of an application to make sure they can function collectively.
Regression Testing
Ensure whether the addition of new features causes a decline in the functionality of an application. It is typically repeated after each build.
Stress Testing
Assesses the strength of software by testing how much load i can take before reaching a breaking point.
Security Testing
Ensures software is free of potential vulnerabilities, knows flaws and security loopholes that might affect the user system and data.
Performance Testing
Digital transformation is the process of using digital technologies to create new — or modify existing — business processes, culture, and customer experiences to meet changing business and market requirements.
Acceptance Testing
Business collaboration is creating purposeful connections, both internally and externally, to achieve goals or solve problems through sharing varied skill sets, strengths, and perspectives.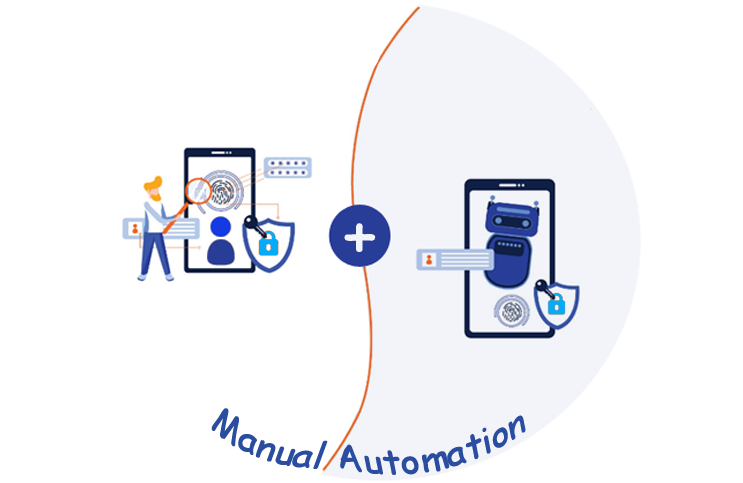
We Execute Manual & Automation Testing
Manual Testing: Manual testing is performed without using any automation tool or any script. In this type, the tester takes over the role of an end-user and tests the software to identify any unexpected behavior or bug. There are different stages for manual testing such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing. Testers use test plans, test cases, or test scenarios to test software to ensure the completeness of testing. Manual testing also includes exploratory testing, as testers explore the software to identify errors in it.
Automation Testing: Tester writes scripts and uses another software to test the product. This process involves the automation of a manual process. Automation Testing is used to re-run the test scenarios quickly and repeatedly, that were performed manually in manual testing. Apart from regression testing, automation testing is also used to test the application from a load, performance, and stress point of view. It increases the test coverage, improves accuracy, and saves time and money when compared to manual testing.
